728x90
반응형
SMALL
데이터 입력 파이프라인 구축
TensorFlow Hub는 다양한 BERT 계열의 모델을 제공한다. 각 모델에는 해당하는 전처리 계층이 함께 제공된다. 리소스에서 이러한 모델과 해당 전처리 계층에 대해 더 자세히 알 수 있다. 런타임을 짧게 하기 위해 원래 BERT 모델의 더 작은 변형을 사용한다.
# Define TF Hub paths to the BERT encoder and its preprocessor
bert_model_path = (
"https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/small_bert/bert_en_uncased_L-2_H-256_A-4/1"
)
bert_preprocess_path = "https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/bert_en_uncased_preprocess/3"
def make_bert_preprocessing_model(sentence_features, seq_length=128):
"""Returns Model mapping string features to BERT inputs.
Args:
sentence_features: A list with the names of string-valued features.
seq_length: An integer that defines the sequence length of BERT inputs.
Returns:
A Keras Model that can be called on a list or dict of string Tensors
(with the order or names, resp., given by sentence_features) and
returns a dict of tensors for input to BERT.
"""
input_segments = [
tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(), dtype=tf.string, name=ft)
for ft in sentence_features
]
# Tokenize the text to word pieces.
bert_preprocess = hub.load(bert_preprocess_path)
tokenizer = hub.KerasLayer(bert_preprocess.tokenize, name="tokenizer")
segments = [tokenizer(s) for s in input_segments]
# Optional: Trim segments in a smart way to fit seq_length.
# Simple cases (like this example) can skip this step and let
# the next step apply a default truncation to approximately equal lengths.
truncated_segments = segments
# Pack inputs. The details (start/end token ids, dict of output tensors)
# are model-dependent, so this gets loaded from the SavedModel.
packer = hub.KerasLayer(
bert_preprocess.bert_pack_inputs,
arguments=dict(seq_length=seq_length),
name="packer",
)
model_inputs = packer(truncated_segments)
return keras.Model(input_segments, model_inputs)
bert_preprocess_model = make_bert_preprocessing_model(["text_1", "text_2"])
# keras.utils.plot_model(bert_preprocess_model, show_shapes=True, show_dtype=True)idx = np.random.choice(len(train_df))
row = train_df.iloc[idx]
sample_text_1, sample_text_2 = row["text_1"], row["text_2"]
print(f"Text 1: {sample_text_1}")
print(f"Text 2: {sample_text_2}")
test_text = [np.array([sample_text_1]), np.array([sample_text_2])]
text_preprocessed = bert_preprocess_model(test_text)
print("Keys : ", list(text_preprocessed.keys()))
print("Shape Word Ids : ", text_preprocessed["input_word_ids"].shape)
print("Word Ids : ", text_preprocessed["input_word_ids"][0, :16])
print("Shape Mask : ", text_preprocessed["input_mask"].shape)
print("Input Mask : ", text_preprocessed["input_mask"][0, :16])
print("Shape Type Ids : ", text_preprocessed["input_type_ids"].shape)
print("Type Ids : ", text_preprocessed["input_type_ids"][0, :16])Keys : ['input_type_ids', 'input_mask', 'input_word_ids']
Shape Word Ids : (1, 128)
Word Ids : tf.Tensor(
[ 101 2057 2018 2256 2034 12185 1997 25682 9609 2006 5958 1010
2206 2062 2084 1037], shape=(16,), dtype=int32)
Shape Mask : (1, 128)
Input Mask : tf.Tensor([1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1], shape=(16,), dtype=int32)
Shape Type Ids : (1, 128)
Type Ids : tf.Tensor([0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0], shape=(16,), dtype=int32)def dataframe_to_dataset(dataframe):
columns = ["image_1_path", "image_2_path", "text_1", "text_2", "label_idx"]
dataframe = dataframe[columns].copy()
labels = dataframe.pop("label_idx")
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((dict(dataframe), labels))
ds = ds.shuffle(buffer_size=len(dataframe))
return dsresize = (128, 128)
bert_input_features = ["input_word_ids", "input_type_ids", "input_mask"]
def preprocess_image(image_path):
extension = tf.strings.split(image_path)[-1]
image = tf.io.read_file(image_path)
if extension == b"jpg":
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image, 3)
else:
image = tf.image.decode_png(image, 3)
image = tf.image.resize(image, resize)
return image
def preprocess_text(text_1, text_2):
text_1 = tf.convert_to_tensor([text_1])
text_2 = tf.convert_to_tensor([text_2])
output = bert_preprocess_model([text_1, text_2])
output = {feature: tf.squeeze(output[feature]) for feature in bert_input_features}
return output
def preprocess_text_and_image(sample):
image_1 = preprocess_image(sample["image_1_path"])
image_2 = preprocess_image(sample["image_2_path"])
text = preprocess_text(sample["text_1"], sample["text_2"])
return {"image_1": image_1, "image_2": image_2, "text": text}batch_size = 32
auto = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
def prepare_dataset(dataframe, training=True):
ds = dataframe_to_dataset(dataframe)
if training:
ds = ds.shuffle(len(train_df))
ds = ds.map(lambda x, y: (preprocess_text_and_image(x), y)).cache()
ds = ds.batch(batch_size).prefetch(auto)
return ds
train_ds = prepare_dataset(train_df)
validation_ds = prepare_dataset(val_df, False)
test_ds = prepare_dataset(test_df, False)
모델 빌드
최종 모델은 텍스트 대응물과 함께 두 개의 이미지를 받아들인다. 이미지가 모델에 직접 공급되는 동안 텍스트 입력은 먼저 전처리된 다음에 모델로 만들어진다. 개별 임베딩을 추출한 후 동일한 공간에 투영된다. 마지막으로, 그들의 투영은 연결되어 최종 분류 계층에 공급된다.
이는 다음 클래스와 관련된 다중 클래스 분류 문제이다.
|
def project_embeddings(
embeddings, num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate
):
projected_embeddings = keras.layers.Dense(units=projection_dims)(embeddings)
for _ in range(num_projection_layers):
x = tf.nn.gelu(projected_embeddings)
x = keras.layers.Dense(projection_dims)(x)
x = keras.layers.Dropout(dropout_rate)(x)
x = keras.layers.Add()([projected_embeddings, x])
projected_embeddings = keras.layers.LayerNormalization()(x)
return projected_embeddingsdef create_vision_encoder(
num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate, trainable=False
):
# Load the pre-trained ResNet50V2 model to be used as the base encoder.
resnet_v2 = keras.applications.ResNet50V2(
include_top=False, weights="imagenet", pooling="avg"
)
# Set the trainability of the base encoder.
for layer in resnet_v2.layers:
layer.trainable = trainable
# Receive the images as inputs.
image_1 = keras.Input(shape=(128, 128, 3), name="image_1")
image_2 = keras.Input(shape=(128, 128, 3), name="image_2")
# Preprocess the input image.
preprocessed_1 = keras.applications.resnet_v2.preprocess_input(image_1)
preprocessed_2 = keras.applications.resnet_v2.preprocess_input(image_2)
# Generate the embeddings for the images using the resnet_v2 model
# concatenate them.
embeddings_1 = resnet_v2(preprocessed_1)
embeddings_2 = resnet_v2(preprocessed_2)
embeddings = keras.layers.Concatenate()([embeddings_1, embeddings_2])
# Project the embeddings produced by the model.
outputs = project_embeddings(
embeddings, num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate
)
# Create the vision encoder model.
return keras.Model([image_1, image_2], outputs, name="vision_encoder")def create_text_encoder(
num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate, trainable=False
):
# Load the pre-trained BERT model to be used as the base encoder.
bert = hub.KerasLayer(bert_model_path, name="bert",)
# Set the trainability of the base encoder.
bert.trainable = trainable
# Receive the text as inputs.
bert_input_features = ["input_type_ids", "input_mask", "input_word_ids"]
inputs = {
feature: keras.Input(shape=(128,), dtype=tf.int32, name=feature)
for feature in bert_input_features
}
# Generate embeddings for the preprocessed text using the BERT model.
embeddings = bert(inputs)["pooled_output"]
# Project the embeddings produced by the model.
outputs = project_embeddings(
embeddings, num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate
)
# Create the text encoder model.
return keras.Model(inputs, outputs, name="text_encoder")def create_multimodal_model(
num_projection_layers=1,
projection_dims=256,
dropout_rate=0.1,
vision_trainable=False,
text_trainable=False,
):
# Receive the images as inputs.
image_1 = keras.Input(shape=(128, 128, 3), name="image_1")
image_2 = keras.Input(shape=(128, 128, 3), name="image_2")
# Receive the text as inputs.
bert_input_features = ["input_type_ids", "input_mask", "input_word_ids"]
text_inputs = {
feature: keras.Input(shape=(128,), dtype=tf.int32, name=feature)
for feature in bert_input_features
}
# Create the encoders.
vision_encoder = create_vision_encoder(
num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate, vision_trainable
)
text_encoder = create_text_encoder(
num_projection_layers, projection_dims, dropout_rate, text_trainable
)
# Fetch the embedding projections.
vision_projections = vision_encoder([image_1, image_2])
text_projections = text_encoder(text_inputs)
# Concatenate the projections and pass through the classification layer.
concatenated = keras.layers.Concatenate()([vision_projections, text_projections])
outputs = keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax")(concatenated)
return keras.Model([image_1, image_2, text_inputs], outputs)
multimodal_model = create_multimodal_model()
# keras.utils.plot_model(multimodal_model, show_shapes=True)
모델 학습
multimodal_model.compile(
optimizer="adam", loss="sparse_categorical_crossentropy", metrics="accuracy"
)
history = multimodal_model.fit(train_ds, validation_data=validation_ds, epochs=10)
모델 평가
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
class_names = ["Contradictory", "Implies", "NoEntailment"]
_, acc = classifier_model.evaluate(test_ds)
print(f"Accuracy on the test set: {round(acc * 100, 2)}%.")Accuracy on the test set: 45.0%.def detailed_test_eval(model):
prediction_labels = np.argmax(model.predict(test_ds), 1)
print(classification_report(test_labels, prediction_labels, target_names=class_names))
return pd.DataFrame(confusion_matrix(test_labels, prediction_labels),
index=class_names, columns=class_names)
detailed_test_eval(classifier_model)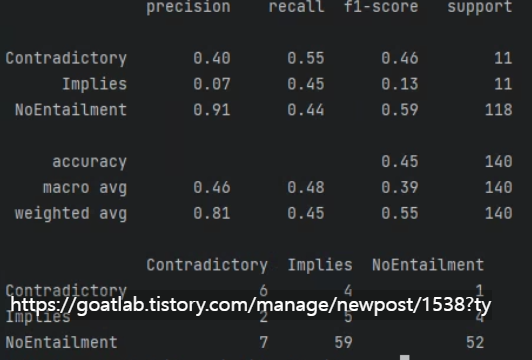
728x90
반응형
LIST
'Python Library > Keras' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Keras] 모델 플롯 유틸리티 (0) | 2024.04.02 |
|---|---|
| [Keras] 멀티모달 함의 분류 (1) (0) | 2024.03.30 |
| [Keras] ImageDataGenerator class weight (0) | 2023.09.08 |
| [Keras] tflite 변환 (0) | 2022.11.24 |
| [Keras] ImageDataGenerator (0) | 2022.08.20 |



